How to Estimation Continuous Time Stochastic Processes
Continuous-time Processes¶
The stochastic.processes.continuous module provides classes for generating discretely sampled continuous-time stochastic processes.
-
stochastic.processes.continuous.BesselProcess -
stochastic.processes.continuous.BrownianBridge -
stochastic.processes.continuous.BrownianExcursion -
stochastic.processes.continuous.BrownianMeander -
stochastic.processes.continuous.BrownianMotion -
stochastic.processes.continuous.CauchyProcess -
stochastic.processes.continuous.FractionalBrownianMotion -
stochastic.processes.continuous.GammaProcess -
stochastic.processes.continuous.GeometricBrownianMotion -
stochastic.processes.continuous.InverseGaussianProcess -
stochastic.processes.continuous.MixedPoissonProcess -
stochastic.processes.continuous.MultifractionalBrownianMotion -
stochastic.processes.continuous.PoissonProcess -
stochastic.processes.continuous.SquaredBesselProcess -
stochastic.processes.continuous.VarianceGammaProcess -
stochastic.processes.continuous.WienerProcess
- class
stochastic.processes.continuous.BesselProcess( dim=1, t=1, rng=None ) [source]¶ -
Bessel process.
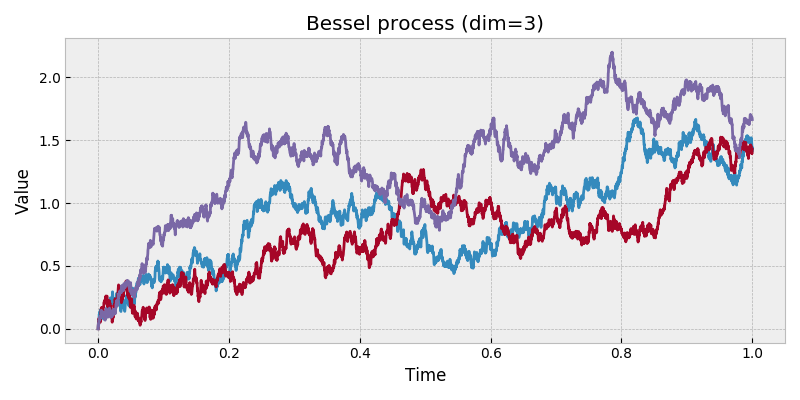
The Bessel process is the Euclidean norm of an \(n\)-dimensional Wiener process, e.g. \(\|\mathbf{W}_t\|\)
Generate Bessel process realizations using
dimindependent Brownian motion processes on the interval \([0,t]\)- Parameters
-
-
dim (int) – the number of underlying independent Brownian motions to use
-
t (float) – the right hand endpoint of the time interval \([0,t]\) for the process
-
rng (numpy.random.Generator) – a custom random number generator
-
-
sample( n ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization.
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments to generate
-
sample_at( times ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization using specified times.
- Parameters
-
times – a vector of increasing time values at which to generate the realization
- property
t¶ -
End time of the process.
-
times( n )¶ -
Generate times associated with n increments on [0, t].
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments
- class
stochastic.processes.continuous.BrownianBridge( b=0, t=1, rng=None ) [source]¶ -
Brownian bridge.
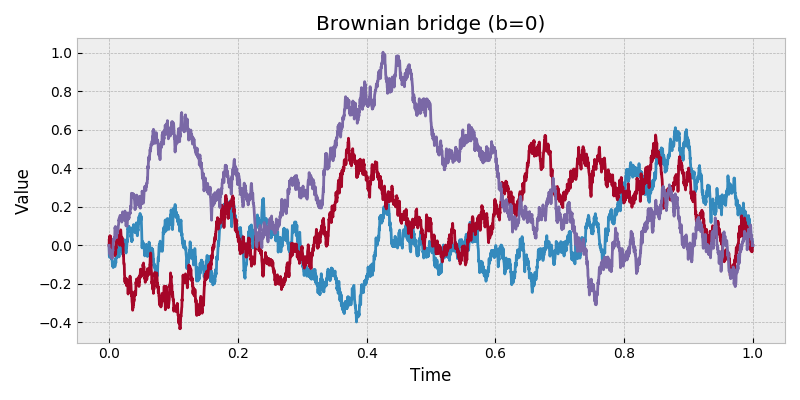
A Brownian bridge is a Brownian motion with a conditional value on the right endpoint of the process.
- Parameters
-
-
b (float) – the right endpoint value of the Brownian bridge at time t
-
t (float) – the right hand endpoint of the time interval \([0,t]\) for the process
-
rng (numpy.random.Generator) – a custom random number generator
-
- property
b¶ -
Right endpoint value.
-
sample( n ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization.
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments to generate
-
sample_at( times, b=None ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization using specified times.
- Parameters
-
-
times – a vector of increasing time values at which to generate the realization
-
b (float) – the right endpoint value for
times[-1]
-
- property
t¶ -
End time of the process.
-
times( n )¶ -
Generate times associated with n increments on [0, t].
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments
- class
stochastic.processes.continuous.BrownianExcursion( t=1, rng=None ) [source]¶ -
Brownian excursion.
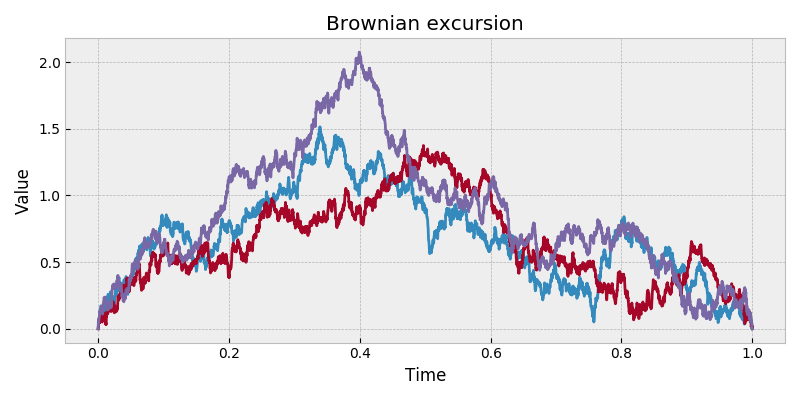
A Brownian excursion is a Brownian bridge from (0, 0) to (t, 0) which is conditioned to be nonnegative on the interval [0, t].
Generated using method by
-
Biane, Philippe. "Relations entre pont et excursion du mouvement Brownien reel." Ann. Inst. Henri Poincare 22, no. 1 (1986): 1-7.
-
Vervaat, Wim. "A relation between Brownian bridge and Brownian excursion." The Annals of Probability (1979): 143-149.
- Parameters
-
-
t (float) – the right hand endpoint of the time interval \([0,t]\) for the process
-
rng (numpy.random.Generator) – a custom random number generator
-
-
sample( n ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization.
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments to generate.
-
sample_at( times ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization using specified times.
- Parameters
-
times – a vector of increasing time values at which to generate the realization
- property
t¶ -
End time of the process.
-
times( n )¶ -
Generate times associated with n increments on [0, t].
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments
-
- class
stochastic.processes.continuous.BrownianMeander( t=1, rng=None ) [source]¶ -
Brownian meander process.
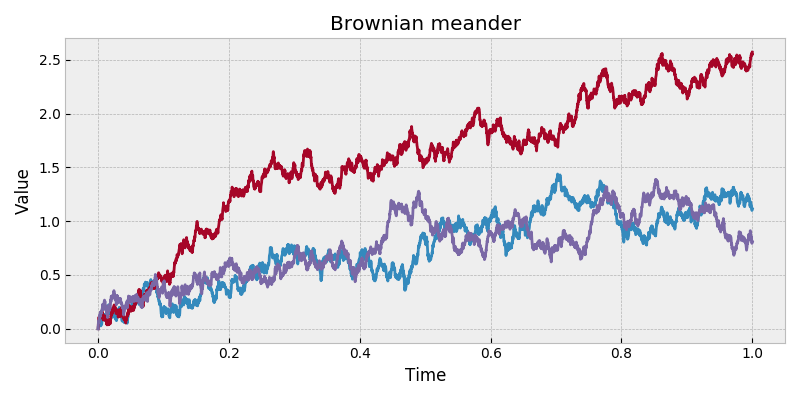
A Brownian motion conditioned such that the process is nonnegative.
Generated using method by
-
Williams, David. "Decomposing the Brownian path." Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society 76, no. 4 (1970): 871-873.
-
Imhof, J-P. "Density factorizations for Brownian motion, meander and the three-dimensional Bessel process, and applications." Journal of Applied Probability 21, no. 3 (1984): 500-510.
- Parameters
-
-
t (float) – the right hand endpoint of the time interval \([0,t]\) for the process
-
rng (numpy.random.Generator) – a custom random number generator
-
-
sample( n, b=None ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization.
- Parameters
-
-
n (int) – the number of increments to generate
-
b (float) – the nonnegative right hand endpoint of the meander. If not provided, one is randomly selected from a \(\sqrt{2E}\) random variable where \(E\) is exponential.
-
-
sample_at( times, b=None ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization using specified times.
- Parameters
-
-
times – a vector of increasing time values at which to generate the realization
-
b (float) – the right endpoint value for
times[-1]. If not provided, one is randomly selected from a \(\sqrt{2tE}\) random variable where \(E\) is exponential and \(t\) istimes[-1].
-
- property
t¶ -
End time of the process.
-
times( n )¶ -
Generate times associated with n increments on [0, t].
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments
-
- class
stochastic.processes.continuous.BrownianMotion( drift=0, scale=1, t=1, rng=None ) [source]¶ -
Brownian motion.
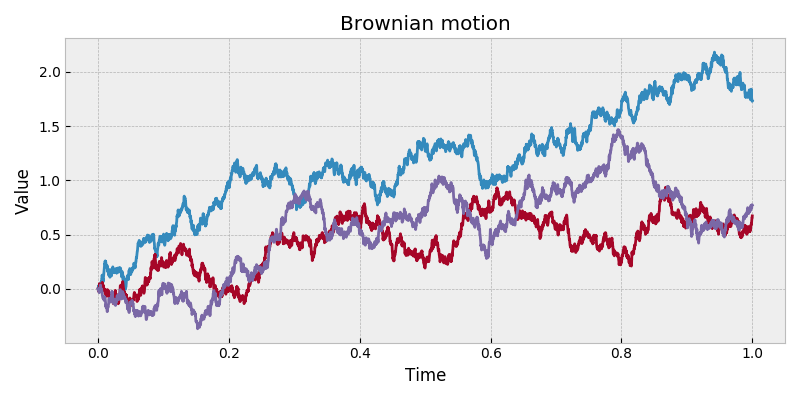
A standard Brownian motion (discretely sampled) has independent and identically distributed Gaussian increments with variance equal to increment length. Non-standard Brownian motion includes a linear drift parameter and scale factor.
- Parameters
-
-
drift (float) – rate of change of the expected value
-
scale (float) – scale factor of the Gaussian process
-
t (float) – the right hand endpoint of the time interval \([0,t]\) for the process
-
rng (numpy.random.Generator) – a custom random number generator
-
- property
drift¶ -
Drift parameter.
-
sample( n ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization.
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments to generate
-
sample_at( times ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization using specified times.
- Parameters
-
times – a vector of increasing time values at which to generate the realization
- property
scale¶ -
Scale parameter.
- property
t¶ -
End time of the process.
-
times( n )¶ -
Generate times associated with n increments on [0, t].
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments
- class
stochastic.processes.continuous.CauchyProcess( t=1, rng=None ) [source]¶ -
Symmetric Cauchy process.
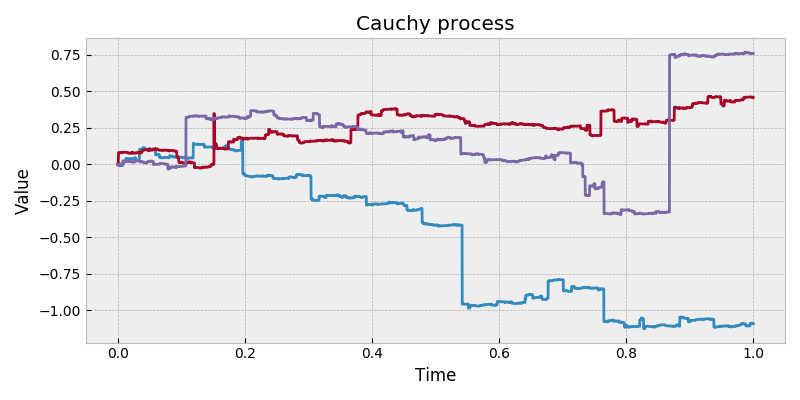
The symmetric Cauchy process is a Brownian motion with a Levy subordinator using location parameter 0 and scale parameter \(t^2/2\).
- Parameters
-
-
t (float) – the right hand endpoint of the time interval \([0,t]\) for the process
-
rng (numpy.random.Generator) – a custom random number generator
-
-
sample( n ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization.
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments to generate.
-
sample_at( times ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization using specified times.
- Parameters
-
times – a vector of increasing time values at which to generate the realization
- property
t¶ -
End time of the process.
-
times( n )¶ -
Generate times associated with n increments on [0, t].
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments
- class
stochastic.processes.continuous.FractionalBrownianMotion( hurst=0.5, t=1, rng=None ) [source]¶ -
Fractional Brownian motion process.
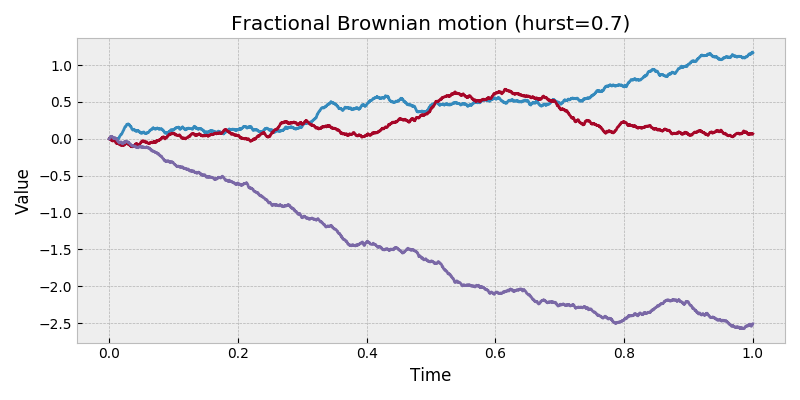
A fractional Brownian motion (discretely sampled) has correlated Gaussian increments defined by Hurst parameter \(H\). When \(H = 1/2\), the process is a standard Brownian motion. When \(H > 1/2\), the increments are positively correlated. When \(H < 1/2\), the increments are negatively correlated.
Hosking's method:
-
Hosking, Jonathan RM. "Modeling persistence in hydrological time series using fractional differencing." Water resources research 20, no. 12 (1984): 1898-1908.
Davies Harte method:
-
Davies, Robert B., and D. S. Harte. "Tests for Hurst effect." Biometrika 74, no. 1 (1987): 95-101.
- Parameters
-
-
hurst (float) – the Hurst parameter on the interval (0, 1)
-
t (float) – the right hand endpoint of the time interval \([0,t]\) for the process
-
rng (numpy.random.Generator) – a custom random number generator
-
- property
hurst¶ -
Hurst parameter.
-
sample( n ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization.
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments to generate
- property
t¶ -
End time of the process.
-
times( n )¶ -
Generate times associated with n increments on [0, t].
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments
-
- class
stochastic.processes.continuous.GammaProcess( mean=None, variance=None, rate=None, scale=None, t=1, rng=None ) [source]¶ -
Gamma process.
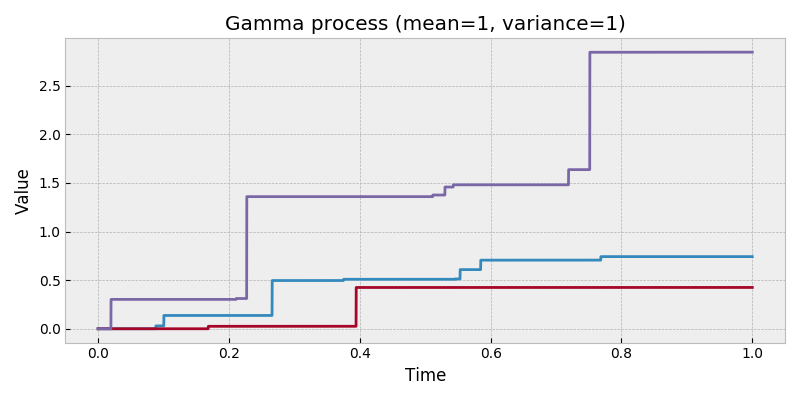
A Gamma process (discretely sampled) is the summation of stationary independent increments which are distributed as gamma random variables. This class supports instantiation using the mean/variance parametrization or the rate/scale parametrization.
- Parameters
-
-
mean (float) – mean increase per unit time; supply with
variance -
variance (float) – variance of increase per unit time; supply with
mean -
rate (float) – the rate of jump arrivals; supply with
scale -
scale (float) – the size of the jumps; supple with
rate -
t (float) – the right hand endpoint of the time interval \([0,t]\) for the process
-
rng (numpy.random.Generator) – a custom random number generator
-
- property
mean¶ -
Mean increase per unit time.
- property
rate¶ -
Rate of jump arrivals.
-
sample( n ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization.
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments to generate
-
sample_at( times ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization at specified times.
- Parameters
-
times – a vector of increasing time values at which to generate the realization
- property
scale¶ -
Scale parameter for jump sizes.
- property
t¶ -
End time of the process.
-
times( n )¶ -
Generate times associated with n increments on [0, t].
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments
- property
variance¶ -
Variance of increase per unit time.
- class
stochastic.processes.continuous.GeometricBrownianMotion( drift=0, volatility=1, t=1, rng=None ) [source]¶ -
Geometric Brownian motion process.
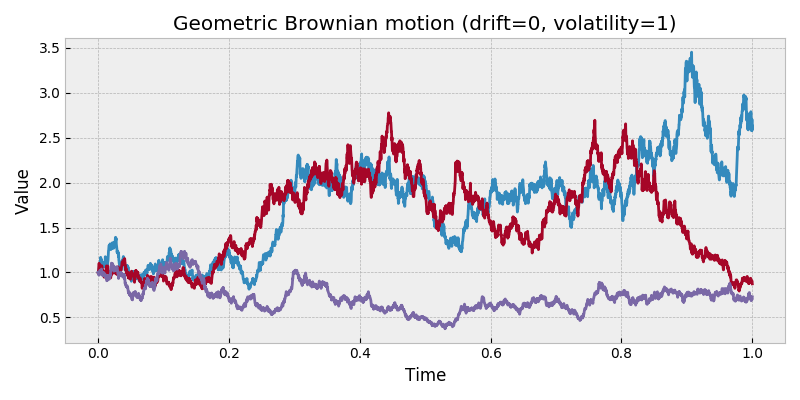
A geometric Brownian motion \(S_t\) is the analytic solution to the stochastic differential equation with Wiener process \(W_t\):
\[dS_t = \mu S_t dt + \sigma S_t dW_t\]
and can be represented with initial value \(S_0\) in the form:
\[S_t = S_0 \exp \left( \left( \mu - \frac{\sigma^2}{2} \right) t + \sigma W_t \right)\]
- Parameters
-
-
drift (float) – the parameter \(\mu\)
-
volatility (float) – the parameter \(\sigma\)
-
t (float) – the right hand endpoint of the time interval \([0,t]\) for the process
-
rng (numpy.random.Generator) – a custom random number generator
-
- property
drift¶ -
Geometric Brownian motion drift parameter.
-
sample( n, initial=1 ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization.
- Parameters
-
-
n (int) – the number of increments to generate.
-
initial (float) – the initial value of the process \(S_0\).
-
-
sample_at( times, initial=1 ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization using specified times.
- Parameters
-
-
times – a vector of increasing time values at which to generate the realization
-
initial (float) – the initial value of the process \(S_0\).
-
- property
t¶ -
End time of the process.
-
times( n )¶ -
Generate times associated with n increments on [0, t].
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments
- property
volatility¶ -
Geometric Brownian motion volatility parameter.
- class
stochastic.processes.continuous.InverseGaussianProcess( mean=None, scale=1, t=1, rng=None ) [source]¶ -
Inverse Gaussian process.
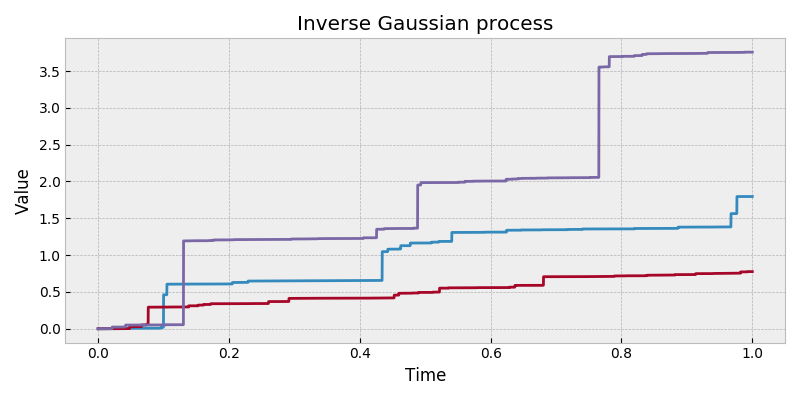
An inverse Gaussian process has independent increments which follow an inverse Gaussian distribution with parameters defined by a monotonically increasing function, \(\Gamma(t)\). E.g. for increment \([s, t]\):
\(\mathcal{IG}(\Gamma(t) - \Gamma(s), \eta(\Gamma(t) - \Gamma(s))^2)\)
Uses a method for generating inverse Gaussian variates from:
-
Michael, John R., William R. Schucany, and Roy W. Haas. "Generating random variates using transformations with multiple roots." The American Statistician 30, no. 2 (1976): 88-90.
- Parameters
-
-
mean (callable) – a callable with one argument \(\Gamma(t)\) such that \(\Gamma(t') > \Gamma(t) \forall t' > t\). Default is the identity function.
-
scale (float) – scale factor of the shape parameter of the inverse gaussian, or \(\eta\) from the above equation.
-
t (float) – the right hand endpoint of the time interval \([0,t]\) for the process
-
rng (numpy.random.Generator) – a custom random number generator
-
- property
mean¶ -
Mean function.
-
sample( n ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization.
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments to generate
-
sample_at( times ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization using specified times.
- Parameters
-
times – a vector of increasing time values at which to generate the realization
- property
scale¶ -
Scale parameter.
- property
t¶ -
End time of the process.
-
times( n )¶ -
Generate times associated with n increments on [0, t].
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments
-
- class
stochastic.processes.continuous.MixedPoissonProcess( rate_func, rate_args=None, rate_kwargs=None, rng=None ) [source]¶ -
Mixed poisson process.
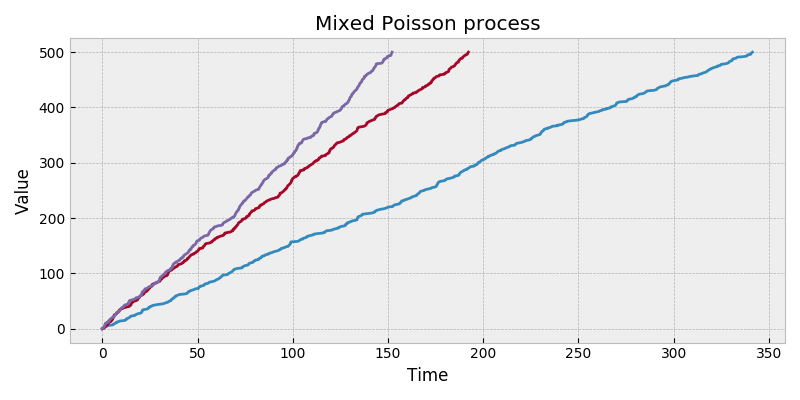
A mixed poisson process is a Poisson process for which the rate is a scalar random variate. The sample method will generate a random variate for the rate before generating a Poisson process realization with the rate. A Poisson process with rate \(\lambda\) is a count of occurrences of i.i.d. exponential random variables with mean \(1/\lambda\). Use the
rateattribute to get the most recently generated random rate.- Parameters
-
-
rate_func (callable) – a callable to generate variates of the random rate
-
rate_args (tuple) – positional args for
rate_func -
rate_kwargs (dict) – keyword args for
rate_func -
rng (numpy.random.Generator) – a custom random number generator
-
- property
rate¶ -
The most recently generated rate.
Attempting to get the rate prior to generating a sample will raise an
AttributeError.
- property
rate_args¶ -
Positional arguments for the rate function.
- property
rate_func¶ -
Current rate's distribution.
- property
rate_kwargs¶ -
Keyword arguments for the rate function.
-
sample( n=None, length=None ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization.
Exactly one of n and length must be provided. Generates a random variate for the rate, then generates a Poisson process realization using this rate.
- Parameters
-
-
n (int) – the number of arrivals to simulate
-
length (int) – the length of time to simulate; will generate arrivals until length is met or exceeded.
-
- class
stochastic.processes.continuous.MultifractionalBrownianMotion( hurst=None, t=1, rng=None ) [source]¶ -
Multifractional Brownian motion process.
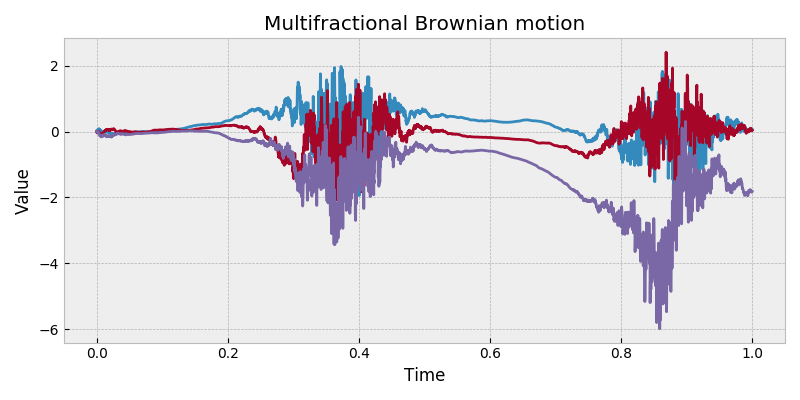
A multifractional Brownian motion generalizes a fractional Brownian motion with a Hurst parameter which is a function of time, \(h(t)\). If the Hurst is constant, the process is a fractional Brownian motion. If Hurst is constant equal to 0.5, the process is a Brownian motion.
Approximate method originally proposed for fBm in
-
Rambaldi, Sandro, and Ombretta Pinazza. "An accurate fractional Brownian motion generator." Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 208, no. 1 (1994): 21-30.
Adapted to approximate mBm in
-
Muniandy, S. V., and S. C. Lim. "Modeling of locally self-similar processes using multifractional Brownian motion of Riemann-Liouville type." Physical Review E 63, no. 4 (2001): 046104.
- Parameters
-
-
hurst (float) – a callable with one argument \(h(t)\) such that \(h(t') \in (0, 1) \forall t' \in [0, t]\). Default is \(h(t) = 0.5\).
-
t (float) – the right hand endpoint of the time interval \([0,t]\) for the process
-
rng (numpy.random.Generator) – a custom random number generator
-
- property
hurst¶ -
Hurst function.
-
sample( n ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization.
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments to generate
- property
t¶ -
End time of the process.
-
times( n )¶ -
Generate times associated with n increments on [0, t].
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments
-
- class
stochastic.processes.continuous.PoissonProcess( rate=1, rng=None ) [source]¶ -
Poisson process.
A Poisson process with rate \(\lambda\) is a count of occurrences of i.i.d. exponential random variables with mean \(1/\lambda\). This class generates samples of times for which cumulative exponential random variables occur.
- Parameters
-
-
rate (float) – the parameter \(\lambda\) which defines the rate of occurrences of the process
-
rng (numpy.random.Generator) – a custom random number generator
-
- property
rate¶ -
Rate parameter.
-
sample( n=None, length=None ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization.
Exactly one of n and length must be provided.
- Parameters
-
-
n (int) – the number of arrivals to simulate
-
length (int) – the length of time to simulate; will generate arrivals until length is met or exceeded.
-
- class
stochastic.processes.continuous.SquaredBesselProcess( dim=1, t=1, rng=None ) [source]¶ -
Squared Bessel process.
The square of a Bessel process: \(\|\mathbf{W}_t\|^2\).
The Bessel process is the Euclidean norm of an \(n\)-dimensional Wiener process, e.g. \(\|\mathbf{W}_t\|\)
- Parameters
-
-
dim (int) – the number of underlying independent Brownian motions to use
-
t (float) – the right hand endpoint of the time interval \([0,t]\) for the process
-
- property
dim¶ -
Dimensions, or independent Brownian motions.
-
sample( n ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization.
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments to generate
-
sample_at( times ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization using specified times.
- Parameters
-
times – a vector of increasing time values at which to generate the realization
- property
t¶ -
End time of the process.
- class
stochastic.processes.continuous.VarianceGammaProcess( drift=0, variance=1, scale=1, t=1, rng=None ) [source]¶ -
Variance Gamma process.
A variance gamma process has independent increments which follow the variance-gamma distribution. It can be represented as a Brownian motion with drift subordinated by a Gamma process:
\[\theta \Gamma(t; 1, \nu) + \sigma W(\Gamma(t; 1, \nu))\]
- Parameters
-
-
drift (float) – the drift parameter of the Brownian motion, or \(\theta\) above
-
variance (float) – the variance parameter of the Gamma subordinator, or \(\nu\) above
-
scale (float) – the scale parameter of the Brownian motion, or \(\sigma\) above
-
t (float) – the right hand endpoint of the time interval \([0,t]\) for the process
-
rng (numpy.random.Generator) – a custom random number generator
-
- property
drift¶ -
Drift parameter.
-
sample( n ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization.
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments to generate
-
sample_at( times ) [source]¶ -
Generate a realization using specified times.
- Parameters
-
times – a vector of increasing time values at which to generate the realization
- property
scale¶ -
Scale parameter.
- property
t¶ -
End time of the process.
- property
variance¶ -
Variance parameter.
- class
stochastic.processes.continuous.WienerProcess( t=1, rng=None ) [source]¶ -
Wiener process, or standard Brownian motion.
- Parameters
-
-
t (float) – the right hand endpoint of the time interval \([0,t]\) for the process
-
rng (numpy.random.Generator) – a custom random number generator
-
-
sample( n )¶ -
Generate a realization.
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments to generate
-
sample_at( times )¶ -
Generate a realization using specified times.
- Parameters
-
times – a vector of increasing time values at which to generate the realization
- property
t¶ -
End time of the process.
-
times( n )¶ -
Generate times associated with n increments on [0, t].
- Parameters
-
n (int) – the number of increments
Source: https://stochastic.readthedocs.io/en/stable/continuous.html
0 Response to "How to Estimation Continuous Time Stochastic Processes"
Post a Comment